In this article, we discuss securing your AWS Virtual Private Cloud. Now while we discuss this using AWS services, the same principles apply in any cloud whether it be the Azure Cloud, Google Cloud or another cloud. Keeping cloud systems secure is critical to avoid security incidents and outages.
Security requires a layered approach to security, where all layers work together to increase the effectiveness of the solution. You can think of effective security as an onion. Peel off one layer, and there is another layer, followed by another layer. This makes it much harder for hackers and leverages the synergies of how individual components can work together for an excellent solution.
Routing
The first place we will begin is with routing. Yes routing, as it’s nearly impossible to hack something when there is no route or path. Cloud security begins by limiting which routes are available to users on the system. By providing routes only to subnets that need specific reachability, we can immediately provide a layer of security.
Virtualized Local Area Networks (VLANs)
Next, we can segment our internal users with VLANs. A VLAN is effectively a virtual switch or group of virtual switches. Users inside a VLAN can communicate with each other. Users outside of a VLAN cannot communicate with users in another VLAN. The only way communication is allowed between VLANs is by routing. If routing is not enabled between VLANS then users cannot communicate with other VLANs. Think of it this way, we can keep users in the finance department separate from accounting team members, developers, testing environments, and everything else. We can further segment inter-VLAN communication with access control lists to be discussed later. There is no cost to using VLANs and they provide an additional layer of security.
Firewalls
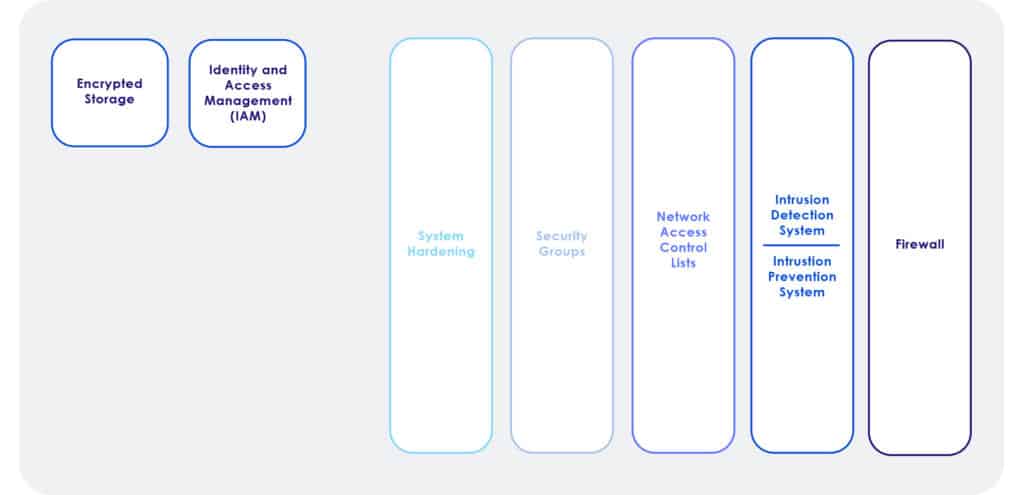
A Firewall is a device or software that builds a strong and secure perimeter around the edge of the network, blocks all incoming traffic by default, and allows specific traffic that is permitted by using a firewall policy. There are some phenomenal commercial firewalls available to use with your VPC from companies such as Cisco, Palo Alto, Fortinet, etc. They are very strong firewalls, that block new attacks through adaptive measures. This means they can look at the suspicious traffic and generate on-demand rules to block traffic that is considered dangerous thereby making commercial firewalls a great option. When it comes to needing enterprise-grade security, we always recommend using a next-generation firewall over a cloud-based firewall like AWS WAF. We only recommend next-generation firewalls as they can adapt with their integrated intrusion detection and prevention capabilities. Solutions like AWS WAF are static and cannot adapt to threats as they are occurring in real-time, which makes them a sub-standard security solution in modern times. Now if the security requirements are not significant, like in a small business, solutions like AWS WAF may be acceptable. However, for enterprise-grade security, use enterprise-grade security solutions which are next-generation firewalls.
Access Control Lists (Network Access Control List)
Network Access Control List or NACL is a packet filter that blocks traffic in and out of the subnets. Access control lists are stateless because it does not watch the way the traffic is coming; it’s only creating some packet inspection rules that allow or deny. All NACLs have a default policy that denies all traffic. When building policies, one must specify the source and the destination address allowed before the deny policy. A wildcard mask could be used to allow or deny all traffic from a network IP address. The wildcard mask tells the router which bits in the IP address need to match the access list and which do not.
Security Group
A security group is effectively a host-based virtual firewall. Security groups are designed to keep unwanted traffic out of the AWS Instance (virtual machine), or service. Security Groups are stateful meaning it watches (keeps track) of inbound traffic. Since the traffic is watched and monitored a security group is stateful, Being stateful the return traffic is allowed back out. This means security groups only need to be defined to permit incoming traffic.
Host-Based Firewall
This is an additional layer of protection on the operating system that can protect against intrusions that may not have been caught by network security. These firewalls protect the system, at least for a period, or maybe completely thwart the attack. Hardening the Host – Most host operating systems are wide open. When most systems boot many services and IP ports are open. These open ports can be used as attack vectors to hack into the systems. All unnecessary services should be disabled to reduce the ability of hackers to hack the systems. Additionally, systems should be patched for the latest security vulnerabilities.
Anti-Malware Protection
All servers should have anti-malware protection against worms and viruses.
Content Delivery Network with DDoS Protection (AWS SHIELD)
Using a content delivery network can substantially protect an organization from a distributed denial of service attack. A content delivery network will only forward legitimate requests to the web server. A content delivery network in most cases will block many of the bad requests hackers use to hack into web applications. Most Content delivery networks also have a great service to provide additional security. AWS has its own branded DDoS protection that can be used on its content delivery network CloudFront. The AWS-branded DDoS protection is AWS Shield. There are two versions of AWS Shield. There is shield basic that provides basic DDoS protection via static policy. Then there is AWS Shield Advanced, which offers adaptive security and provides much better DDoS protection.
Intrusion Preventions/Intrusion Detection System (IPS/IDS)
Intrusion detection and prevention systems provide real-time monitoring of systems. They can identify and stop attacks as they occur. Intrusion detection and prevention systems are devices or software applications that monitor a network or systems for malicious activity or policy violations. They look at known attack behaviors and unknown patterns of behaviors that look suspicious to adapt and stop the activity as needed. They also create rules on demand to stop attacks as they occur. Now next-generation firewalls have this capability, but in very high-security environments it may makes sense to also use dedicated intrusion detection and prevention systems
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
To keep systems secure it’s essential to only provide access to systems to those who need access. Additionally, it’s best to allow access to the least amount of information necessary for people to do their jobs. The military calls this “Need to Know” in tech it’s called the principle of least privilege. Identity and Access Management helps us with this goal.
It is essential to identify who the user is, and what the user can do on the system, and then track the user’s access. This is performed with Identity and access management. Identity and access management can be summarized below:
- Authentication is the identification of who you are as a user
- Authorization defines what you can access
- Accounting records have you done on the system
Identity and access management gives us the ability to provide the correct level of access to our users. So, what is the right level of access? It is the minimal amount of access necessary for people to perform their jobs.
Encryption
Encryption is another component of security. Encryption is a means of securing data by encoding the data in a manner that it can only be read, or decrypted, by those with the correct key. Encryption processes translate data using an algorithm that makes the original information unreadable except for authorized users. Encryption should be used for stored data (encryption at rest) and during the transition (encryption in transit).
In conclusion, security takes a layered approach toward ensuring your system is safe and secure. Each layer works together synchronously to provide a cohesive security solution!
Cloud Architect Career Development Program
We’ll send you a nice letter once per week. No spam.